Designing and interpreting 4D tumour spheroid experiments Alex Browning Biology Diagrams We have incorporated this real-time cell cycle tracking system in to a melanoma 3D in vitro model by generating spheroids initiated from FUCCI melanoma cell lines (10). We have used this system to study dynamic heterogeneity in cell cycle behavior and invasion (10), drug sensitivity (11) and acquired multidrug tolerance in melanoma (12). The cell cycle is driven by precise temporal coordination among many molecular activities. To understand and explore this process, we developed the Cell Cycle Browser (CCB), an interactive web interface based on real-time reporter data collected in proliferating human cells. However, cell cycle analysis has been revolutionized by real-time cell cycle imaging, using the fluorescent ubiquitination-based cell cycle indicator (FUCCI) or similar systems. This genetically encoded system allows spatial and temporal real-time tracking of cell cycle progression of individual cells in a multicellular context.
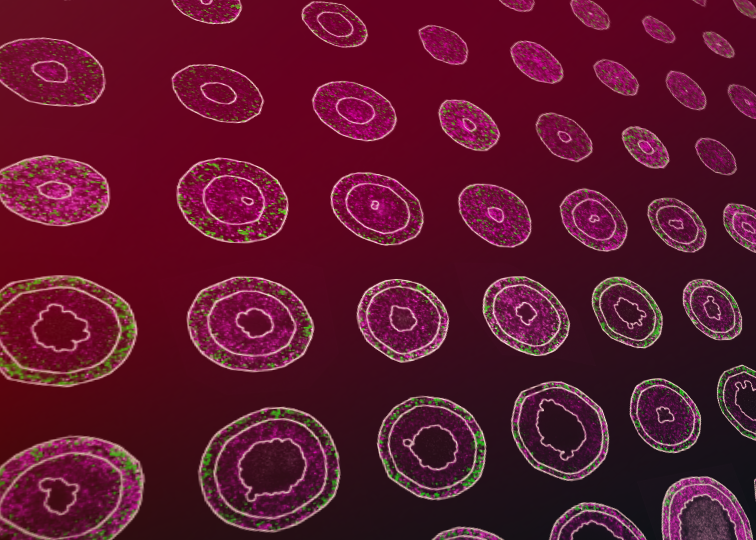
Here we exploit transgenic mice expressing fluorescent cell cycle indicators to longitudinally track the division dynamics of individual CD8(+) T cells. During influenza virus infection in vivo, naive T cells enter a … Real-time tracking of cell cycle progression during CD8+ effector and memory T-cell differentiation Nat Commun . 2015 Feb In this chapter, we describe a technique that allows spatiotemporal real-time tracking of cell cycle progression of individual cells in a multicellular context. The power of this system lies in the use of 3D melanoma spheroids generated from melanoma cells engineered with the fluorescent ubiquitination-based cell cycle indicator (FUCCI However, cell cycle progression has been most commonly assessed by methods that are limited to temporal snapshots or that lack spatial information. Here, we describe a technique that allows spatiotemporal real-time tracking of cell cycle progression of individual cells in a multicellular context. The power of this system lies in the use of 3D

Time Cell Cycle Imaging in a 3D Cell Culture Model of Melanoma ... Biology Diagrams
This not only allows to monitor the cell cycle dynamics, but also tracking cell migration parameters such as trajectory and velocity, as a function of cell cycle state, in a single setup and in real time . Paradoxically, this benefit can also turn into a disadvantage, since it means that the fluorophore used for tracking does not have a

Automatic handling of real-time tracking: Cell-ACDC has real-time tracking to aid with the correction process and it automatically detects which frame was already visited and corrected to avoid that wrong tracking invalidates that frame again.Note that the table contains only software that either uses a deep-learning approach or includes tracking and downstream analysis of growing cell Real-time tracking of cell cycle progression during CD8 + effector and memory T-cell differentiation. Nat. Commun. 6:6301 doi: 10.1038/ncomms7301 (2015). Accession codes. Accessions Real-time tracking of cell cycle progression during CD8 þ effector and memory T-cell differentiation Ichiko Kinjyo 1,w , Jim Qin 1 , Sioh-Yang Tan 1 , Cameron J. Wellard 2,3 , Paulus Mrass 1,w