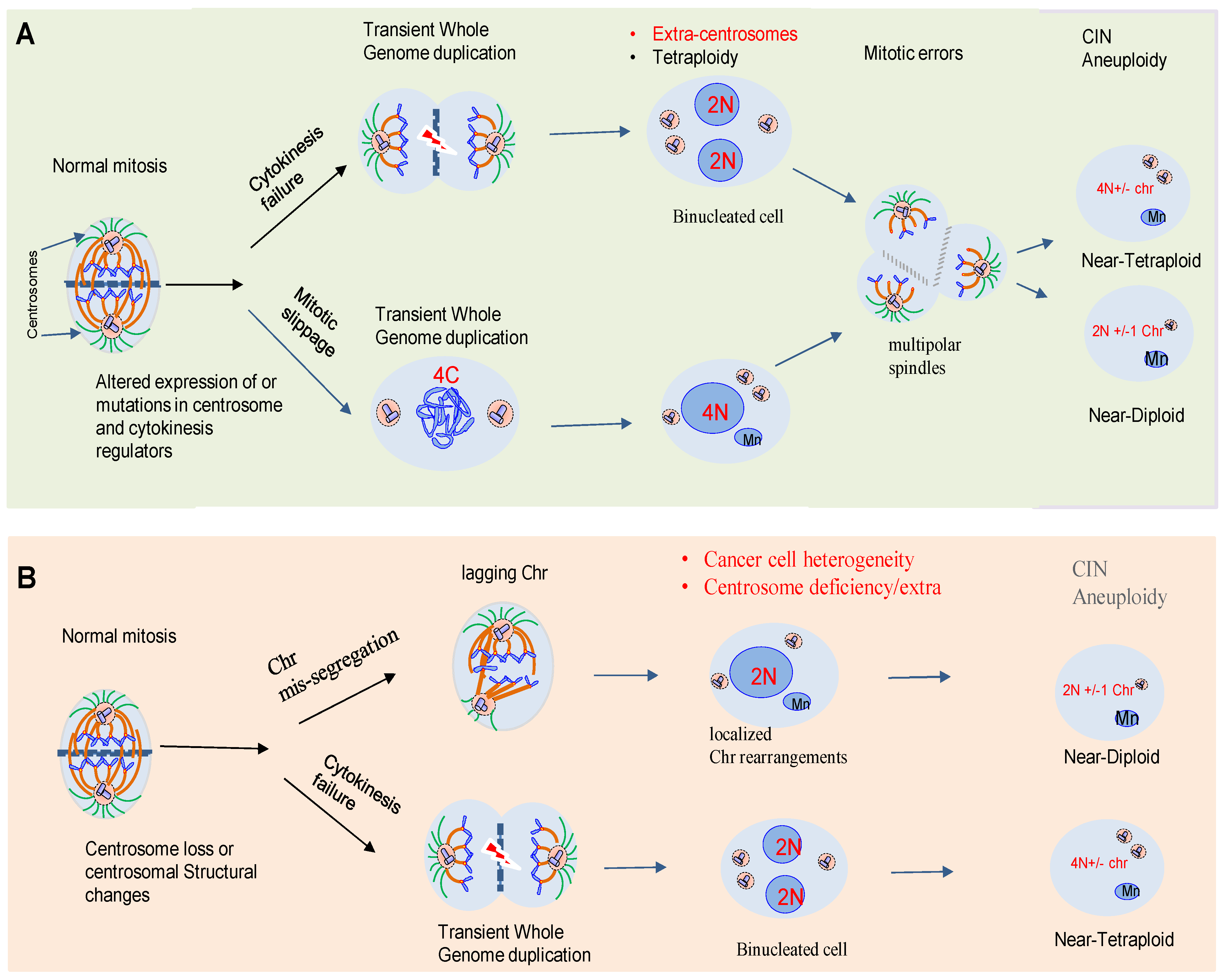
Centrosome Dysfunction in Drosophila Neural Stem Cells Causes Tumors Biology Diagrams Role In Cell Division. Centrosomes are indispensable during cell division, primarily through their orchestration of the mitotic spindle apparatus. This process begins in the prophase of mitosis, where centrosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell, establishing the bipolar spindle necessary for chromosome segregation. Centrosomes were first described by Edouard Van Beneden and named and linked to chromosome segregation by Theodor Boveri around 1870. In the 1960-1980s, electron microscopy studies have revealed the remarkable ultrastructure of a centriole -- a nine-fold symmetrical microtubular assembly that resides within a centrosome and organizes it.

The centrosome serves as the primary microtubule-organizing center in animal cells, playing a crucial role in cell division and ciliogenesis. It becomes a spindle pole in mitotic cells, and it A. Role of the centrosome in spindle formation during mitosis. The centrosome has an important job in making the spindle during mitosis, acting as a center that organizes microtubules to help with the proper arrangement and movement of chromosomes. When mitosis begins, centrosomes change in a key way, with their pericentriolar material (PCM

Centrosomes in mitotic spindle assembly and orientation Biology Diagrams
Before mitosis, centrosomes undergo a process called centrosome maturation, in which they expand in size, increase MT nucleation and form the poles of and Gergely F, Small organelle, big responsibility: the role of centrosomes in development and disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 2014. 369(1650). [PMC free article]

Centrosome separation at the entry of mitosis plays an important role in their normal segregation. Several molecules play a role in centrosome separation. First, the two centrosomes are physically associated by a mesh of fibers composed by rootletin, amongst other components, which are tethered to the proximal end of centrioles, through a Centrosome duplication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle, and by the time a cell enters mitosis, it contains two centrosomes, which will form the poles of the bipolar mitotic spindle. As cells enter mitosis, centrosomes migrate to opposite sides of the nuclear envelope to promote spindle bipolarity to ensure faithful chromosome segregation. In mammalian somatic cells, centrosomes play a key role in spindle formation and spindle shape [15]. During interphase, centrosomes are duplicated at the nuclear envelope.